dna polymerase 1 role in dna replication|enzymes involved in dna replication : 2024-10-05 Roles of DNA polymerases and other replication enzymes. Leading and lagging strands and Okazaki fragments. See more Map Browser includes data and services of JSC Latvia's State Forests, Jāņa Seta Map Publishers, Ltd., Nature Conservation Agency of Latvia, Latvian Geospatial Information Agency.
0 · why is dna replication important
1 · what is the role of dna polymerase i
2 · what is the difference between dna polymerase 1 and 111
3 · role of dna ligase in dna replication
4 · enzymes involved in dna replication
5 · dna replication diagram
6 · dna polymerase 1 vs 3
7 · dna ligase function in dna replication
8 · More
110 HPGliscor LV. X - 141/146 - Ultra Rare Legends Awakened Pokemon MP [eBay] $20.31: 2021-09-14
dna polymerase 1 role in dna replication*******Roles of DNA polymerases and other replication enzymes. Leading and lagging strands and Okazaki fragments. See more
In the replication process, RNase H removes the RNA primer (created by primase) from the lagging strand and then polymerase I fills in the necessary nucleotides between the Okazaki fragments (see DNA replication) in a 5'→3' direction, proofreading for mistakes as it goes. It is a template-dependent enzyme—it only adds nucleotides that correctly base pair with an existing DNA strand acting as a template. It is crucial that these nucleotides are in the proper orientation and geomet.Flap Endonuclease 1 (FEN 1) also plays a role in removing ‘flaps’ of nucleic acid from the 5’ ends of the fragments often displaced by polymerase as it replaces the replication .
dna polymerase 1 role in dna replication enzymes involved in dna replicationFlap Endonuclease 1 (FEN 1) also plays a role in removing ‘flaps’ of nucleic acid from the 5’ ends of the fragments often displaced by polymerase as it replaces the replication .dna polymerase 1 role in dna replicationAs discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a . Figure 9.2.1 9.2. 1: The two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning the sequence of bases in one strand can be used to create the correct sequence of .Scientists have since identified a total of five different DNA polymerases in E. coli, each with a specialized role. For example, DNA polymerase III does most of the elongation work, adding . Roles of DNA polymerase I in leading and lagging-strand replication defined by a high-resolution mutation footprint of ColE1 plasmid replication Jennifer M. .Base-Pairing Underlies DNA Replication and DNA Repair. As discussed briefly in Chapter 1, DNA templating is the process in which the nucleotide sequence of a DNA strand (or selected portions of a DNA strand) is . Major Enzymes. The process of DNA replication is catalyzed by a type of enzyme called DNA polymerase (poly meaning many, mer meaning pieces, and –ase meaning enzyme; so an enzyme . It is generally accepted that the main role of Pol ε is in leading-strand DNA replication, although it is still under debate whether Pol ε or Pol δ is the main polymerase in this function 143 .Figure 9.2.1 9.2. 1: The two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning the sequence of bases in one strand can be used to create the correct sequence of bases in the other strand. Because of the complementarity of the two strands, having one strand means that it is possible to recreate the other strand.DNA polymerase I plays an essential role in the replication process in E. coli, but it is not the enzyme that catalyzes the overall DNA polymerization of the replicating strands. The enzyme that accomplishes this is a less abundant enzyme: polymerase III (pol III).
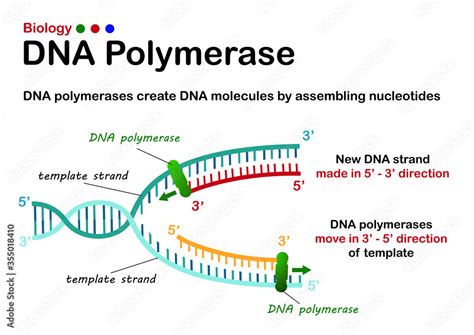
DNA polymerase I (pol I) processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions. However, it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. Here, we addres .enzymes involved in dna replication DNA polymerase I (pol I) processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions. However, it is unclear how pol I and pol III work together during replication and repair or how extensive pol I processing of Okazaki fragments is in vivo. Here, we addres . Functions of DNA Polymerase in prokaryotic cell. DNA Polymerase Ι. is a repair polymerase with both 3’ to 5’ and 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity. polymerase activity in 5’ to 3’ direction. this enzyme is involved in the processing of Okazaki fragments generated by lagging strand synthesis. DNA Polymerase ΙΙ.
These are equivalent to the origin of replication in E. coli. The number of DNA polymerases in eukaryotes is much more than prokaryotes: 14 are known, of which five are known to have major roles during replication and have been well studied. They are known as pol α, pol β, pol γ, pol δ, and pol ε. The essential steps of replication are the .
Polymerase Chain Reaction uses DNA polymerases to repeatedly replicate DNA in-vitro and has numerous applications in diagnosis, sequencing, and recombinant DNA technology. The formation of complementary DNA (cDNA) can also be considered as an example of a wider application of the enzymes involved in DNA .This page titled 14.4: DNA Replication in Prokaryotes is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax. DNA replication has been extremely well studied in prokaryotes primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available. E. coli has 4.6 million base pairs in a single ..An enzyme, DNA polymerase, catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA molecules from deoxyribonucleotides (the building blocks of DNA). It is crucial in living organisms’ DNA replication, repair, and recombination processes. DNA polymerases attach new nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing DNA strand by forming phosphodiester bonds . In this review, the structure and function of all 15 mammalian DNA polymerases from families B, Y, X, and A will be reviewed and discussed with special emphasis on the insights gleaned from recently published atomic resolution structures. Keywords: DNA polymerase, Replication, DNA repair, Structural biology, DNA synthesis.
DNA polymerase θ (Pol θ) exhibits properties typical of translesion and repair synthesis; however, its physiological function remains elusive. Here, the authors show that Pol θ plays a role in .
Abstract. DNA polymerase I (pol I) processes RNA primers during lagging-strand synthesis and fills small gaps during DNA repair reactions. However, it is u 1 Department of Microbiology and Environmental Toxicology, University of California Santa Cruz, 1156 High Street Santa Cruz, CA 95060, 2 Biomedical Engineering Department and . Studies of unchallenged DNA replication in yeast systems, using mutations and genomic ribonucleotides as biomarkers of polymerase activity, indicate that Pol δ conducts the majority of .
DNA Polymerase δ (Pol δ) is the main enzyme for replication in eukaryotes. It is a multi-subunit enzyme with three core subunits (p125, p50, and p66) and accessory factors. Apart from replication, Pol δ also has 3’→5’ exonuclease activity for proofreading. DNA Polymerase ε (Pol ε) is another multi-subunit enzyme with four subunits. Abstract. In eukaryotic cells, DNA replication is carried out by the coordinated action of three DNA polymerases (Pols), Pol α, δ, and ε. In this report, we describe the reconstitution of the human four-subunit Pol ε and characterization of its catalytic properties in comparison with Pol α and Pol δ. Human Pol ε holoenzyme is a .
Leading & lagging strands DNA polymerase can only build the new strand in one direction (5’ to 3’ direction) As DNA is ‘unzipped’ from the 3’ towards the 5’ end, DNA polymerase will attach to the 3’ end of the original strand and move towards the replication fork (the point at which the DNA molecule is splitting into two template strands)

DNA polymerase I (or Pol I) is an enzyme that participates in the process of prokaryotic DNA replication. Discovered by Arthur Kornberg in 1956,[1] it was the first known DNA polymerase (and the first known of any kind of polymerase). It was initially characterized in E. coli and is ubiquitous in prokaryotes. In E. coli and many other bacteria . In addition to its role in DNA repair and replication, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) also has varied roles in controlling the functions of various components of the transcription machinery.
3. The role of PCNA in normal DNA replication In eukaryotes, DNA replication is an extraordinarily complex, dynamic, multi-stage process that initiates at origins of replication [53–56].Before an origin can fire, it must be licensed. Origin licensing occurs during late M .
LOUIS VUITTON Official USA site - Explore the World of Louis Vuitton, . Key Holders and Bag Charms. Home Textile. Tech Accessories. All Fashion Jewelry. Necklaces and Pendants. Bracelets. Rings. Earrings. Modern Classics. LV Trainer. All Shoes. Sneakers. Loafers and Moccasins. Buckles and Lace-Ups.
dna polymerase 1 role in dna replication|enzymes involved in dna replication











